Improve the Biosynthesis of Baicalein and Scutellarein via Manufacturing Self-Assembly Enzyme Reactor In Vivo
A research paper《Improve the Biosynthesis of Baicalein and Scutellarein via Manufacturing Self-Assembly Enzyme Reactor In Vivo》was published in ACS Synthetic Biology on April 21th, 2021.
Baicalein and scutellarein are two valuable ingredients of Scutellariabaicalensis Georgi and Erigeron karvinskianus,respectively. Their chemical structures are similar and structural difference is on the presence of a 4’-hydroxy group on the B ring of scutellarein, which is lacking on baicalein. These two ingredients are showed with extensive pharmacological activities and are potentional to be developed as a cardiovascular or antibacterial drug. However, there still remains facing with the extremelly poor yield from plant materials. It is highly promisiming to develop a biotechnological production platform for baicalein and scutellarein. Previously, our group reported the construction of parallelly synthetic pathway to product baicalein and scutellarein in E.coli, however, the metabolic obstruction was obsreved in the fermention, resulting in the accumulation of pahtway intermadiates and the low yield of the desired products.
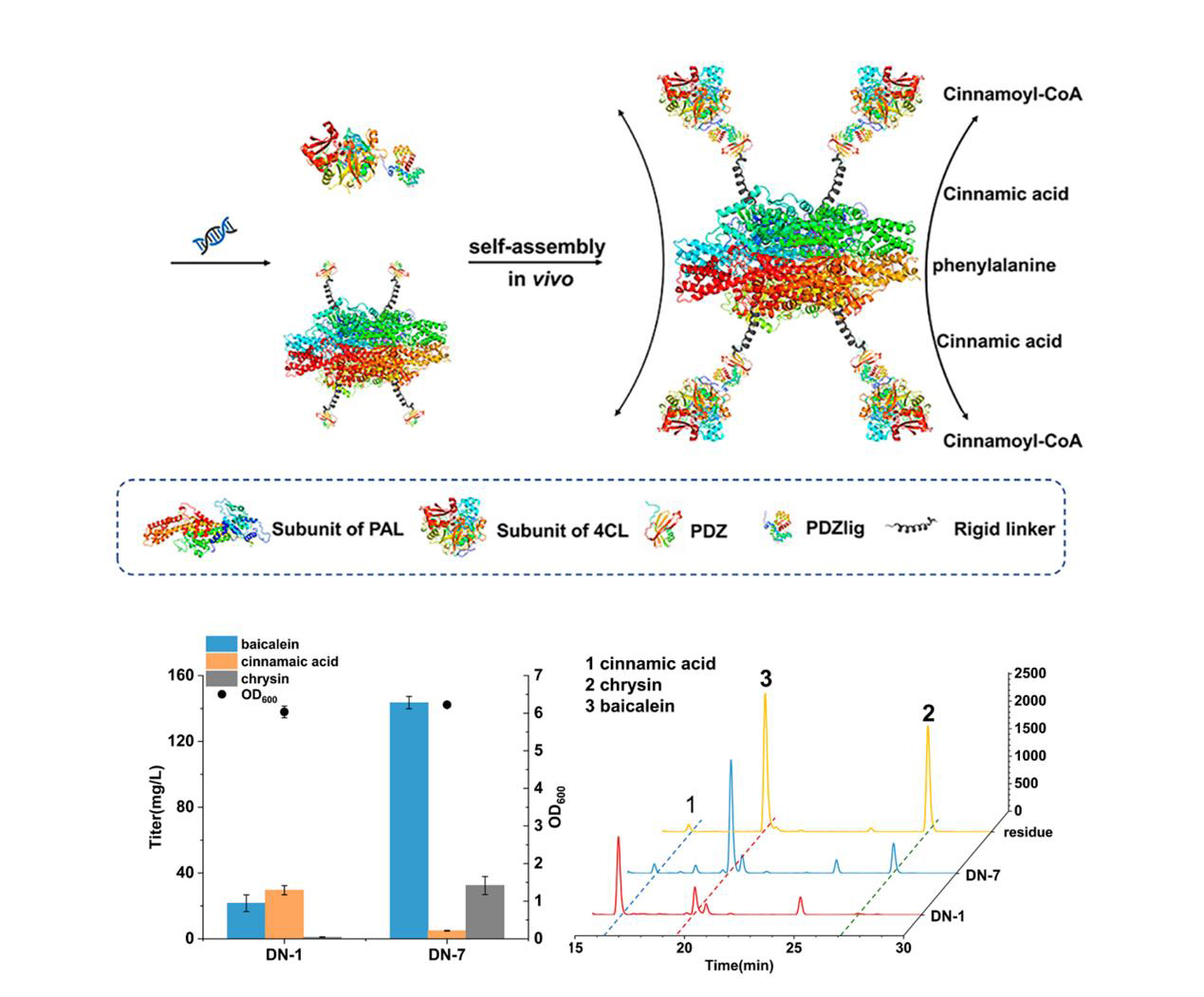
In this study, the authors break the bottleneck by developing a sequential self-assembly enzyme reactor, in which an interacting protein pairs (PDZ and PDZ ligand) were used to perform dual-enzyme self-assembly of RtPAL (Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase, RtPAL) and Pc4CL (4-coumarate-CoA ligase, Pc4CL). This strategy effectively reduced the accumulation of intermediates and successfully promoted the titer of baicalein by 6.6-fold (from 21.6 to 143.5 mg/L) and that of scutellarein by 1.4-fold (from 84.3 to 120.4 mg/L), respectively. The engineered strains produced 271.6 mg/L baicalein and 288.9 mg/L scutellarein in a fed-batch culture, respectively . In addition, this work also achieved the synthesis of baicalein from glucose for the first time, and the strain was able to produce 214.1 mg/L of baicalein through fed-batch fermentation . This system has several potential advantages: (I) increasing the local concentration of the substrate, (II) decreasing the transit times of intermediates, (III) circumventing unfavorable enzymes reaction kinetics, (IV) increasing metabolic flux, which could be used in the procudtion of other added-valuable metabolites in microbe.
The work was corporated and finished by CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Science and East China University of Science and Technology. Professor Yong Wang and Yuhong Ren are the corresponding authors, and Dongni Ji is the first author of this paper. This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFA0900600), Shanghai Outstanding Academic Leader Program (20XD1404400), the Strategic Priority Research Program ‘Molecular Mechanism of Plant Growth and Development’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB27020202), Chinese Academy of Sciences Strategic Leader B project.
Figure 1. Production improvement of baicalein and scutellarein through a self-assembled enzyme reactor.
Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00606
Contact:
Dr. Yong Wang, Professor
Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences , Chinese Academic of Sciences
Email: yongwang@cemps.ac.cn